India Avasara Academy Uses Sustainable Air Flow Design In Architecture
The Avasara Academy for Girls in Lavale, India designed a school building built on the foundation of locally available resources and sustainable practices while providing a comfortable atmosphere and open learning environment for young women’s education.

The building is designed with exhaust cavities that push air flow naturally from earth ducts controlling temperature fluctuation throughout the school and eventually rises out of the roof through solar chimneys.
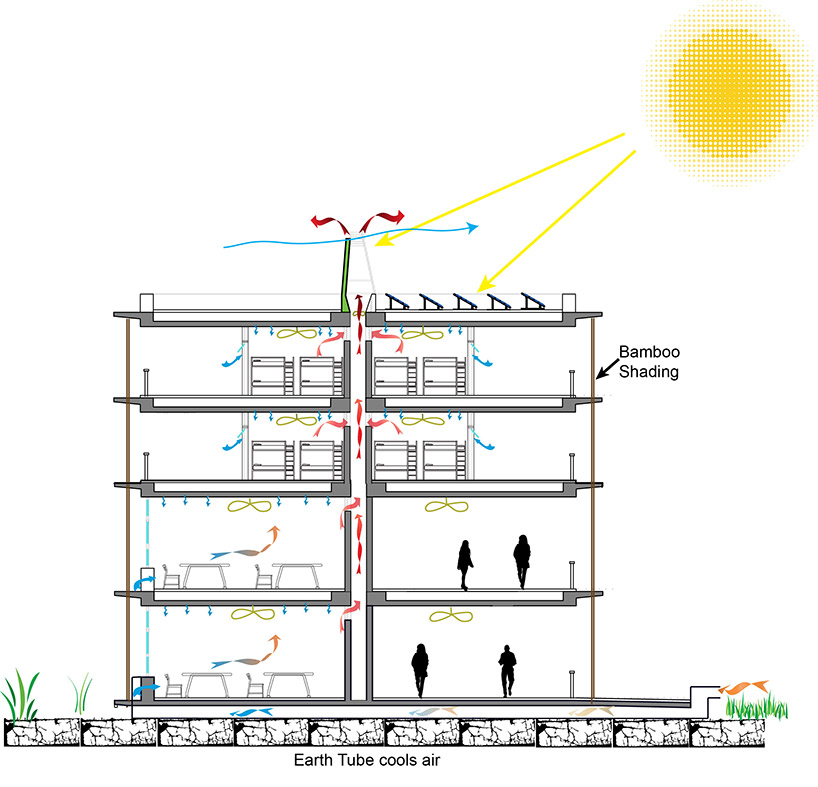
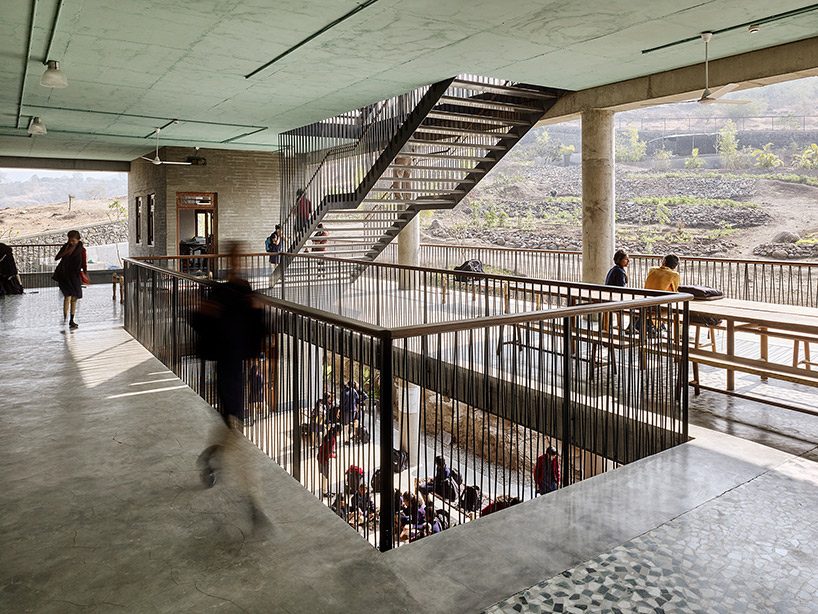
The center of the building is completely open, allowing air to circulate freely and creates a more communal and free thinking environment for the students attending the academy. This natural system uses no mechanical system to provide year around internal cooling, an impressive feat considering the warm and humid climate where the school is located.

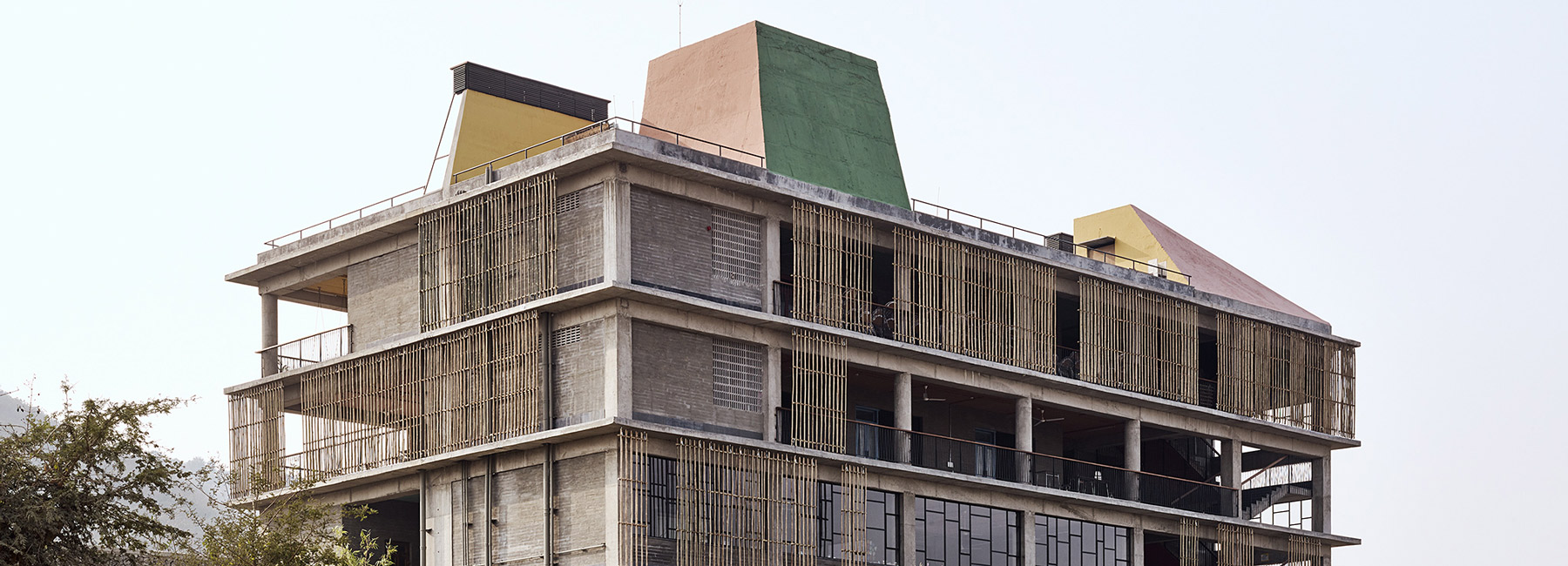
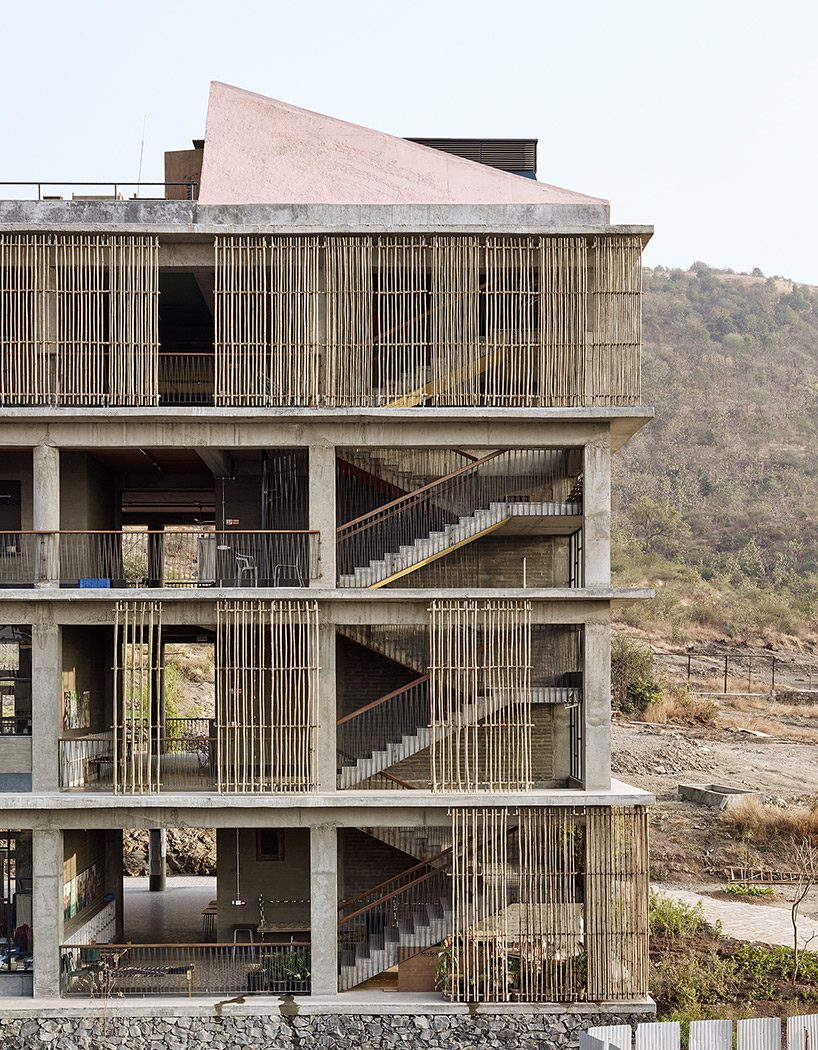
The largest structure consists of classrooms and facilities, it is built using concrete with each ceiling of every classroom painted a different pastel color and bamboo panels to provide shade for subtle privacy all the while still allowing natural light to enter the building and the surrounding landscape to be visible. The campus is 4.3 acres in size and consists of a collection of simple structures surrounded by informal walkways, gardens and terraces.

Designed by Mumbai-based firm Case Design alongside Transsolar Klima Engineering, they were able to make Avasara Academy a net-zero energy building, meaning it is environmentally friendly and contributes less overall greenhouse gas to the atmosphere compared with non net-zero energy buildings.